【Redis】Redis 配置文件详解
Units 单位
配置大小单位,开头定义了一些基本的度量单位,只支持bytes,不支持bit,大小写不敏感。
# Redis configuration file example. # # Note that in order to read the configuration file, Redis must be # started with the file path as first argument: # # ./redis-server /path/to/redis.conf # Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specify # it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth: # # 1k => 1000 bytes # 1kb => 1024 bytes # 1m => 1000000 bytes # 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes # 1g => 1000000000 bytes # 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes # # units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same.
INCLUDES 包含
类似jsp中的include,多实例的情况可以把公用的配置文件提取出来
################################## INCLUDES ################################### # Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you # have a standard template that goes to all Redis servers but also need # to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include # other files, so use this wisely. # # Note that option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE" # from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed # line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes # at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runtime. # # If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration # options, it is better to use include as the last line. # # include /path/to/local.conf # include /path/to/other.conf
NETWORK 网络相关配置
bind
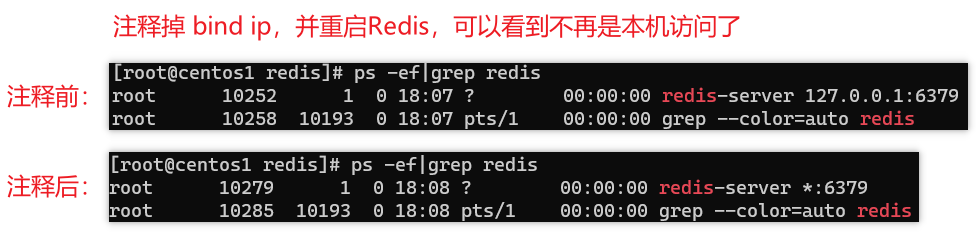
默认情况
bind=127.0.0.1只能接受本机的访问请求不写的情况下,无限制接受任何ip地址的访问
生产环境要写应用服务器的地址,服务器是需要远程访问的。
如果开启了
protected-mode,那么在没有设定bind ip且没有设密码的情况下,Redis只允许接受本机的响应
################################## NETWORK ##################################### # By default, if no "bind" configuration directive is specified, Redis listens # for connections from all available network interfaces on the host machine. # It is possible to listen to just one or multiple selected interfaces using # the "bind" configuration directive, followed by one or more IP addresses. # Each address can be prefixed by "-", which means that redis will not fail to # start if the address is not available. Being not available only refers to # addresses that does not correspond to any network interfece. Addresses that # are already in use will always fail, and unsupported protocols will always BE # silently skipped. # # Examples: # # bind 192.168.1.100 10.0.0.1 # listens on two specific IPv4 addresses # bind 127.0.0.1 ::1 # listens on loopback IPv4 and IPv6 # bind * -::* # like the default, all available interfaces # # ~~~ WARNING ~~~ If the computer running Redis is directly exposed to the # internet, binding to all the interfaces is dangerous and will expose the # instance to everybody on the internet. So by default we uncomment the # following bind directive, that will force Redis to listen only on the # IPv4 and IPv6 (if available) loopback interface addresses (this means Redis # will only be able to accept client connections from the same host that it is # running on). # # IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES # JUST COMMENT OUT THE FOLLOWING LINE. # ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ bind 127.0.0.1 -::1
protected-mode
本机访问保护模式,设置no
# Protected mode is a layer of security protection, in order to avoid that # Redis instances left open on the internet are accessed and exploited. # # When protected mode is on and if: # # 1) The server is not binding explicitly to a set of addresses using the # "bind" directive. # 2) No password is configured. # # The server only accepts connections from clients connecting from the # IPv4 and IPv6 loopback addresses 127.0.0.1 and ::1, and from Unix domain # sockets. # # By default protected mode is enabled. You should disable it only if # you are sure you want clients from other hosts to connect to Redis # even if no authentication is configured, nor a specific set of interfaces # are explicitly listed using the "bind" directive. protected-mode no
port
端口号,默认为6379
# Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 (IANA #815344). # If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket. port 6379
tcp-backlog
设置tcp的backlog,backlog其实是一个连接队列,backlog队列总和=未完成三次握手队列 + 已经完成三次握手队列。
在高并发环境下需要一个高backlog值来避免慢客户端连接问题。
Linux内核会将这个值减小到
/proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn的值(128),所以需要确认增大/proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn和/proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog(128)两个值来达到想要的效果。
# TCP listen() backlog. # # In high requests-per-second environments you need a high backlog in order # to avoid slow clients connection issues. Note that the Linux kernel # will silently truncate it to the value of /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn so # make sure to raise both the value of somaxconn and tcp_max_syn_backlog # in order to get the desired effect. tcp-backlog 511
timeout
一个空闲的客户端维持多少秒会关闭,0表示关闭该功能。即永不关闭。
# Close the connection after a client is idle for N seconds (0 to disable) timeout 0
tcp-keepalive
对访问客户端的一种心跳检测,每个n秒检测一次,单位为秒。
如果设置为0,则不会进行Keepalive检测。
建议设置成60。
# TCP keepalive. # # If non-zero, use SO_KEEPALIVE to send TCP ACKs to clients in absence # of communication. This is useful for two reasons: # # 1) Detect dead peers. # 2) Force network equipment in the middle to consider the connection to be # alive. # # On Linux, the specified value (in seconds) is the period used to send ACKs. # Note that to close the connection the double of the time is needed. # On other kernels the period depends on the kernel configuration. # # A reasonable value for this option is 300 seconds, which is the new # Redis default starting with Redis 3.2.1. tcp-keepalive 300
GENERAL 通用
daemonize
是否为后台进程,设置为 yes
守护进程,后台启动
# By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it. # Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized. # When Redis is supervised by upstart or systemd, this parameter has no impact. daemonize yes
pidfile
存放pid文件的位置,每个实例会产生一个不同的pid文件
# If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup # and removes it at exit. # # When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is # specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid file # is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid". # # Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it # nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally. # # Note that on modern Linux systems "/run/redis.pid" is more conforming # and should be used instead. pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
loglevel
指定日志记录级别,Redis总共支持四个级别: debug 、 verbose 、 notice 、 warning ,默认为 notice
四个级别根据使用阶段来选择,生产环境选择 notice 或者 warning
# Specify the server verbosity level. # This can be one of: # debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing) # verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level) # notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably) # warning (only very important / critical messages are logged) loglevel notice
logfile
日志文件名称
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force # Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard # output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null logfile ""
databases
设定库的数量 默认16,默认数据库为0,可以使用 SELECT <dbid> 命令在连接上指定数据库id
# Set the number of databases. The default database is DB 0, you can select # a different one on a per-connection basis using SELECT <dbid> where # dbid is a number between 0 and 'databases'-1 databases 16
SECURITY 安全
设置密码
访问密码的查看、设置和取消
在命令中设置密码,只是临时的。重启redis服务器,密码就还原了。
永久设置,需要再配置文件中进行设置。
# IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6 "requirepass" is just a compatibility # layer on top of the new ACL system. The option effect will be just setting # the password for the default user. Clients will still authenticate using # AUTH <password> as usually, or more explicitly with AUTH default <password> # if they follow the new protocol: both will work. # # The requirepass is not compatable with aclfile option and the ACL LOAD # command, these will cause requirepass to be ignored. # # requirepass foobared
临时设置密码:
127.0.0.1:6379> config get requirepass 1) "requirepass" 2) "" 127.0.0.1:6379> config set requirepass "123456" OK 127.0.0.1:6379> config get requirepass 1) "requirepass" 2) "123456"
LIMITS 限制
maxclients
设置redis同时可以与多少个客户端进行连接,默认情况下为10000个客户端。
如果达到了此限制,redis则会拒绝新的连接请求,并且向这些连接请求方发出“max number of clients reached”以作回应。
# Set the max number of connected clients at the same time. By default # this limit is set to 10000 clients, however if the Redis server is not # able to configure the process file limit to allow for the specified limit # the max number of allowed clients is set to the current file limit # minus 32 (as Redis reserves a few file descriptors for internal uses). # # Once the limit is reached Redis will close all the new connections sending # an error 'max number of clients reached'. # # IMPORTANT: When Redis Cluster is used, the max number of connections is also # shared with the cluster bus: every node in the cluster will use two # connections, one incoming and another outgoing. It is important to size the # limit accordingly in case of very large clusters. # # maxclients 10000
maxmemory
设置redis可以使用的内存量,一旦到达内存使用上限,redis将会试图移除内部数据,移除规则可以通过 maxmemory-policy 来指定。
建议设置,否则可能内存占满,造成服务器宕机。
如果redis无法根据移除规则来移除内存中的数据,或者设置了“不允许移除”,那么redis则会针对那些需要申请内存的指令返回错误信息,比如SET、LPUSH等。
但是对于无内存申请的指令,仍然会正常响应,比如GET等。如果redis是主redis(说明redis有从redis),那么在设置内存使用上限时,需要在系统中留出一些内存空间给同步队列缓存,只有在设置的是“不移除”的情况下,才不用考虑这个因素。
# Set a memory usage limit to the specified amount of bytes. # When the memory limit is reached Redis will try to remove keys # according to the eviction policy selected (see maxmemory-policy). # # If Redis can't remove keys according to the policy, or if the policy is # set to 'noeviction', Redis will start to reply with errors to commands # that would use more memory, like SET, LPUSH, and so on, and will continue # to reply to read-only commands like GET. # # This option is usually useful when using Redis as an LRU or LFU cache, or to # set a hard memory limit for an instance (using the 'noeviction' policy). # # WARNING: If you have replicas attached to an instance with maxmemory on, # the size of the output buffers needed to feed the replicas are subtracted # from the used memory count, so that network problems / resyncs will # not trigger a loop where keys are evicted, and in turn the output # buffer of replicas is full with DELs of keys evicted triggering the deletion # of more keys, and so forth until the database is completely emptied. # # In short... if you have replicas attached it is suggested that you set a lower # limit for maxmemory so that there is some free RAM on the system for replica # output buffers (but this is not needed if the policy is 'noeviction'). # # maxmemory <bytes>
maxmemory-policy
volatile-lru:使用LRU算法移除key,只对设置了过期时间的键;(最近最少使用)allkeys-lru:在所有集合key中,使用LRU算法移除keyvolatile-random:在过期集合中移除随机的key,只对设置了过期时间的键allkeys-random:在所有集合key中,移除随机的keyvolatile-ttl:移除那些TTL值最小的key,即那些最近要过期的keynoeviction:不进行移除,针对写操作,只是返回错误信息
# MAXMEMORY POLICY: how Redis will select what to remove when maxmemory # is reached. You can select one from the following behaviors: # # volatile-lru -> Evict using approximated LRU, only keys with an expire set. # allkeys-lru -> Evict any key using approximated LRU. # volatile-lfu -> Evict using approximated LFU, only keys with an expire set. # allkeys-lfu -> Evict any key using approximated LFU. # volatile-random -> Remove a random key having an expire set. # allkeys-random -> Remove a random key, any key. # volatile-ttl -> Remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL) # noeviction -> Don't evict anything, just return an error on write operations. # # LRU means Least Recently Used # LFU means Least Frequently Used # # Both LRU, LFU and volatile-ttl are implemented using approximated # randomized algorithms. # # Note: with any of the above policies, when there are no suitable keys for # eviction, Redis will return an error on write operations that require # more memory. These are usually commands that create new keys, add data or # modify existing keys. A few examples are: SET, INCR, HSET, LPUSH, SUNIONSTORE, # SORT (due to the STORE argument), and EXEC (if the transaction includes any # command that requires memory). # # The default is: # # maxmemory-policy noeviction
maxmemory-samples
设置样本数量,LRU算法和最小TTL算法都并非是精确的算法,而是估算值,所以可以设置样本的大小,redis默认会检查这么多个key并选择其中LRU的那个。
一般设置3到7的数字,数值越小样本越不准确,但性能消耗越小。
# LRU, LFU and minimal TTL algorithms are not precise algorithms but approximated # algorithms (in order to save memory), so you can tune it for speed or # accuracy. By default Redis will check five keys and pick the one that was # used least recently, you can change the sample size using the following # configuration directive. # # The default of 5 produces good enough results. 10 Approximates very closely # true LRU but costs more CPU. 3 is faster but not very accurate. # # maxmemory-samples 5
猜你喜欢
- 【Redis】redis除了做缓存还能做什么
- redis应该说是目前最受欢迎的nosql数据库之一了。redis通常被作为缓存组件,用作缓存数据。不过,除了可以缓存数据,其实redis可以做的事还有很多。下面列举几例,供大家参考。1、最新列表例如新闻列表页面最新的新闻列表,如果总数量很大的情况下,尽量不要使用select a from A limit 10,尝试redis的 LPUSH命令构建List,一个个顺序都塞进去就可以啦。不过万一内存清掉了咋办? (推荐学习:Red
- 【Redis】redis分布式缓存
- 目录一、单机安装Redis。二、Redis主从集群。2.1.集群结构2.2.准备实例和配置2.3.启动2.4.开启主从关系2.5.测试三、搭建哨兵集群。3.1.集群结构3.2.准备实例和配置3.3.启动3.4.测试四、搭建分片集群。4.1.集群结构4.2.准备实例和配置4.3.启动4.4.创建集群4.5.测试五、单点redis的问题。六、Redis持久化。1)RDB持久化。2) AOF持久化。3)RDB和AOF的对比。七、Redis主从。1)搭建主从架构。2) 主从数据同步原
- 【Redis】Redis对象——内存回收,对象共享和空转时长
- 一. 内存回收 因为C语言不具备内存回收功能,所以Redis在自己的对象系统中构建了一个引用计数技术实现内存回收机制。通过这一机制,程序可以通过跟踪对象的引用计数信息,在适当的时候自动释放对象并进行内存回收。 内每一个对象的引用计数信息由redisObject结构的refcount属性记录:typedef struct redisObject {
- 【Redis】Redis与Memcached的区别
- 一、主要区别:1.Redis是一个开源的内存数据结构存储,用作数据库,缓存和消息代理; 2.Memcached是一个免费的开源高性能分布式内存对象缓存系统,它通过减少数据库负载来加速动态Web应用程序。memcached是高性能的分布式内存缓存服务器。 一般使用目的是,通过缓存数据库查询结果,减少数据库访问次数,以提高动态web应用的速度、提高可扩展性。redis是一个开源的内存数据库,它以键值对的形式存储数据。由于数据存储在内存中,因此Redis的速度很快,但是每次重启Redis服务时,其中的
- 【Redis】Redis配置详解
- 目录一、Redis查看当前配置命令二、Redis基本配置三、RDB全量持久化配置(默认开启)四、AOF增量持久化配置五、Redis key过期监听配置六、Redis内存淘汰策略七、总结一、Redis查看当前配置命令# Redis查看当前全部配置信息 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET * # Redis查看当前指定配置信息 127.0.0.1:6379> CONFIG GET 配置名
- 【Redis】Redis中缓存穿透、击穿、雪崩以及解决方案
- 目录一、什么是Redis二、什么是缓存穿透三、什么是缓存击穿四、什么是缓存雪崩一、什么是RedisRedis是一个开源的内存数据存储系统,也是一个高性能的键值存储数据库。它支持多种数据结构,包括字符串、哈希表、列表、集合以及有序集合。Redis的特点是快速、灵活和可扩展。首先,Redis是一个内存数据存储系统,这意味着它将所有数据存储在内存中,因此具有非常快的读写速度。相比于传统的磁盘存储系统,Redis可以提供非常低的读写延迟,使得它非常适合需要快速响应的应用场景,如缓存、实时计算等。其次,R
